What does It Network Security mean?
It Network security requires adhering to protocols to avoid unwanted access, abuse alteration, or denial of a computer network and access network infrastructure. Network security is managed by a It network security administrator or network security engineer.
Network security is also known as computer security. Networks can be private or public and they can be transparent or closed and several elements are active in all layers. It secures and oversees the activities being performed over the network. Learn about top It network security.
What does an It network security professional do?
Network security engineers play a significant role in an enterprise. They are in charge of preparing, designing, and maintaining systems and other controls, including tools for data protection, firewalls, VPN, etc. They may be responsible for evaluating ways of retrieving data or networks damaged by cyber-attacks. They should be alert to the new developments and threats to discourage them.
The Most Effective 10 It Network Security Concepts
Your network faces threats of all shapes and sizes and thus should be prepared to defend, identify and respond to a full range of attacks.
But the reality is that the biggest danger to most companies is not fly-by-night threat actors, but rather attackers that are well-funded and are targeting specific organizations for specific reasons. For that reason, your It network security strategy needs to be able to address the various methods these actors might employ.
Below are some of the 10 types of Network Security Concepts:
- Access Control
- Antivirus
- Data Loss Prevention
- Email Security
- Firewalls
- VPN
- Web Security
- Wireless Security
- Intrusion Prevention Detection
- Network Segmentation
Network Security Concept No.1: Access Control
A means of controlling access to confidential data is access management. Only those who have checked their identities will access the data of an organization through a gateway.

Components
- Access management at high-level concerns limiting resource access. Any access control device has five major components, be it physical or logical.
- The proof of a claim, such as an individual or a computer user’s identity. This may include validating personal identification records, confirming the validity of the website, or checking user credentials for stored information.
- The function of defining resource access rights or privileges. For instance, personnel is commonly permitted to view documents of employees, and this policy is often made public through computer-based access management laws.
- The person or machine can access the resource until authenticated and approved. Adding and disabling security and authorization of users or devices means managing an access management scheme. In certain applications, G Suite or Azure Active Directory sync, the management process can be streamlined.
- Often used to apply the concept of least privilege as part of the access protection. Users may end up having access, e.g., as they shift roles, over time. This risk is reduced by regular audits.
Why do we need this It network security tool?
- It Network security deals with preventing such attacks and securing the stability, credibility, and safety of a company’s computer network. We’ve compiled a few items to be on the lookout for when you choose your security solution for your network.
- Protect and enhance your business assets. Security in networked computers is the value of the information contained in the network. The information is just as necessary and important as other business properties, particularly the company’s sensitive information (from employee social security numbers to confidential client records).
Security services mitigate the risks of companies by preventing security vulnerabilities and court actions that would bankrupt small businesses.
- Comply with governmental regulations −. Businesses use security technology to comply with different regulations, such as Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA), Sarbanes-Oxley Act, Family Educational Rights and Privacy Act (FERPA), Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI-DSS), and Federal Information Security Management Act (FISMA)
- Ensure a safe variety of working environments wherein information sharing is maintained. It Network security provides a robust and safe environment for clients and consumers.
- I assume that computers have the most effect on companies. As long as you are aware of the vulnerabilities presented by computers and have adequate security measures in place, computers can be a valuable asset to your company.
It Network Security Concept No.2: Antivirus
Antivirus apps will defend your computer from internet threats. Antivirus software involves the collection of information flowing across the network to the computers to check for viruses and other threats. It tracks all known risks and looks for patterns of bad behavior within programs. The software program tries to “stop or uninstall ransomware” as soon as possible.
Antivirus security is essential since cyberthreats cannot be exhausted. If you don’t have computer or security software enabled, you may be vulnerable to viruses or have data stolen by other malicious software that will stay undetected.

What aim is for a virus to damage a computer?
If your computer is attacked, your computer can be compromised in several ways.
- Delete files
- harm, or lose files;
- data loss;
- frequent computer crashes;
- extreme computer instability;
- slow the computer down.
Why do we need this network security tool?
- An antivirus program scans files for viruses without removing them. It detects any viruses and then reduces their harmful effects. This is usually done until the virus has worked its way to the heart.
- The pop-up advertisements and spam websites are used by viruses and spyware to infect your computer to infiltrate and damage your files. Antivirus software protects your computer from destructive viruses by blocking its ability to send messages directly to your computer.
- Antivirus software either puts a lock on access or carries out routine checks to identify any potential intruder or hacker software on the network. Antivirus software offers security against hackers at the highest level. You can have to slow down or reboot your computer due to a file-sharing issue with a friend.
- Why did that happen? That is so because the USB drive was a conduit of infection. So, can we abandon our use of removable devices because maybe some of them have malicious software on them? No. For malware protection, just have your computer check all removable media and ensure that none of your personal information is exposed.
- A security program monitors the files that come into the machine. All of those files are placed into a search to make sure they are not harmful or unusual. Viruses encrypted files and data can quickly be transferred to your network and they pose a threat to your files and data. You may also lose your important private data to potentially malicious viruses.
- Accessing unauthorized web pages will place your computer at risk of many cybersecurity threats. Their content could theoretically affect your data and information. When using an antivirus program, you are limited to restricted access to the internet to prevent unwanted networking.
- This is intended to ensure that only secure and innocent websites will bypass all of the computer systems.
Network Security Concept No.3: Network Data Loss Prevention
Data loss prevention network is a technology for protecting the network communications of an enterprise such as email, mobile services, and conventional data-sharing channels such as FTP. Companies use network data loss protection solutions to avoid network loss of confidential information.
These technologies provide businesses with the possibility of properly encrypting data and blocking dangerous communication flows to track, protect and regulate the data flow across their networks.
1. Management and control of email traffic, webmail, web-based applications, HTTP/S, FTP/S, and TCP/IP Usually included network failure protection capable of:
2. Gain control and visibility of webmail’s and FTP, including SSL-enabled sessions
3. Prevent sensitive data loss over the network regardless of port or protocol
4. Inspect sensitive content subjects, messages and attaches for emails
5. Policy-based monitoring and blocking of web applications

Why do we need this network security tool?
Businesses suffer significant financial damages and reputational harm if they lose classified data and other sources of business intelligence. The business case for data loss prevention initiatives (DLP) is currently well understood by companies, and data security is thus becoming the most trending problem. Any of the main reasons a company requires DLP are given below:
- DLP technology offers a 360-degree view of traffic, location, and use of information around the company for IT and security personnel. It is capable of controlling network activities against the security policy of an enterprise and allows you to protect and manage confidential data including PII, financial data, user information, and intellectual property.
- DLP allows the prevention of unintended disclosure of personal information in all platforms and is used in conjunction with supplementary controls. Data can be monitored and reduced significantly in all data lives by DLP.
- To achieve enforcement within particular regions, technology safeguards are becoming vital. These controls are provided by DLP, including policy models and maps to simplify enforcement, resolve specific criteria, and allow measurements to be collected and reported.
- DLP offers revised regulation models and maps that respond to individual criteria, assist in metric collection and reporting and simplify enforcement. Once a policy need has been identified, DLP will modify the policy blueprint on your machine so easily and effectively.
Network Security Concept No.4: Email Security
The word email security is used to shield email content and accounts from unwanted access with any process. Email service providers are subject to email protection controls to protect customer accounts and hacker knowledge. Such safeguards include e-mail servers with strict password and access management mechanisms; secure emails (boxed or in transit), firewalls of web applications, and tools for spam filters.
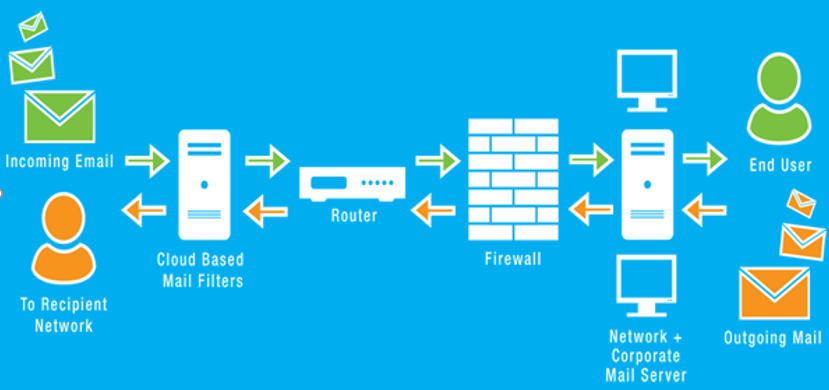
Email is used with hackers as ransomware, spam, and phishing platform. They use misleading messaging to make beneficiaries share sensitive information which leads to identity theft. They attract users to open attachments or click hyperlinks, which install malware on a user’s computer (for example email viruses). Email also is a major entry point for attackers seeking corporate network access and infringing sensitive enterprise data.
Why do we need this network security tool?
- There’s so much at stake these days because of a range of email attacks, therefore nobody wants to send unencrypted communications. Any stranger can access the information found in your mail without encryption. These can be used against you by your opponents. Therefore, it is advisable to encrypt the emails to better secure confidential information, both to avoid business and other threats.
- Could you imagine reading or even transiting the messages you send? Both the username and the password you type will easily be taken. It is therefore necessary to prevent leakage with email encryption of such essential information.
- First of all, you will get an authentic message and only get false, later official messages. The receiver cannot decide if the email address sent to him is changed. If you just removed the post, you don’t even know it was never sent.
- If someone can read the emails that you are sent, or deliver the bogus emails if anyone takes your name and your password to reach his or her email servers. This is called identity fraud and can be stopped if you are encrypted by email.
- This means that although a person sends a specific message, he or she may refuse to deliver that message. This has significant consequences in terms of using email for contracts, e-commerce, corporate correspondence, etc.
Network Security Concept No.5: Firewall
Firewalls closely analyze traffic from unsecured or suspect springs based on pre-established rules and filter traffic to avoid attacks. At the computer entry point, Firewalls guard traffic named ports, where information is shared with external computers. For eg, “Address of source 172.18.1.1 is permitted over port 22 to enter destination 172.18.2.1.”
Consider IP addresses as houses and port numbers as home quarters. The house (destination addresses) may only be entered by trustworthy individuals (source addresses), meaning that people may only enter such rooms (destination ports) inside the house based on whether they are an occupant, child, or invited person.
The owner can enter a room (any port), while the children and visitors may enter a certain number of spaces (specific ports).
Why do we need this network security tool?
- All the advantages of firewall protection begin with network traffic monitoring. Data entering and leaving your applications poses a challenge to your activities. Firewalls use pre-established rules and filters to protect the networks by tracking and evaluating network traffic. You can control your defense level with a well-trained IT team depending on what you see coming into and outside through your firewall.
- There is nothing more rapid or difficult than a virus attack to close down your digital operations. It is important to put the protections in place to keep your networks secure with thousands of new threats every day.The ability to monitor the access points of your device and deter malware attacks is one of the most obvious advantages of firewalls. Depending on the type of infection, the cost of disruption to the infrastructure can be enormously high.
- Regrettably, the rise in companies transitioning to digital operations calls for theft and bad people to do the same. Firewalls are becoming much more critical because of increasing robbery and criminals keeping devices hostage, as hackers are being prevented from illegal access to files, emails, systems, and much more. A firewall can avoid or discourage a hacker from selecting an easier target.
- In a data-driven environment, Spyware can’t hack and get into the networks, a much-needed bonus. For more sophisticated and robust schemes, hackers may also use the entry points to obtain access to the systems. Spyware and Malware—programs to hack your networks, manipulate your machines and steal data—is one of the common ways unwanted users access it. These malicious applications act as a major blockade for firewalls.
- The promotion of privacy is an overall advantage. You provide an atmosphere of privacy that the consumers can trust by working proactively to keep their data and the customers’ data secure. Nobody likes to steal their data especially if it is apparent that action to avoid interference should have been taken.
- Also, improved data security services will provide consumers and customers a strategic edge and sales point. The advantage raises your company’s data sensitivity.
Network Security Concept No.6: VPN
VPN stands for “Virtual Private Network” which defines the possibility to link the network with public networks. VPN encrypts and masks your Internet name. your internet traffics. This makes web tracking and stealing of data more complicated for third parties. Encoding occurs in real-time.
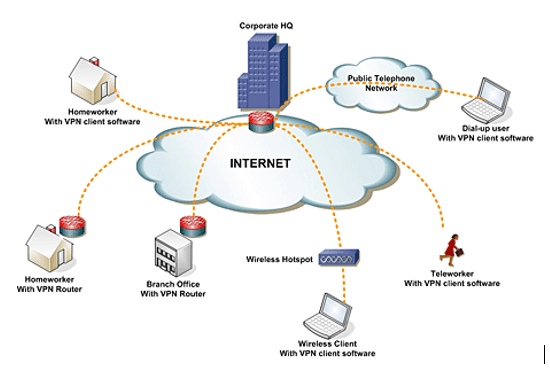
What is the role of a VPN?
A VPN masks an IP address by enabling the network to redirect it from a remote server operated by a VPN host that is specially specified. This makes the VPN registry the root of your data while you are navigating online with a VPN. This makes it impossible for you and others to see which pages you use, which details you to submit and receive online, or which other third parties do not. A VPN functions like a buffer that converts all of the information into “gibberish.” It’d be pointless, even if somebody had their hands on your results.
Why do we need this network security tool?
A VPN link masks and defends the data traffic from external access online. Anyone who has network connectivity and wishes to see unencrypted data should be consulted. This information cannot be deciphered by hackers and cybercriminals using a VPN.
Encoding secure: You use an encoding key to read the data. Without a machine, it would take millions of years to decrypt the code if a brute force attack were to take place. You can also hide your online activities on public networks with the assistance of a VPN.
Shroud your whereabouts: basically, VPN servers act as your online proxies. As the location data are from a server in another world, it is not possible to ascertain the exact location. Moreover, most VPN providers do not save your business logs. On the other hand, certain providers report your behavior but do not pass it on to third parties. This ensures that the user behavior is still shielded from any future record.
Access to regional content: Not always from anywhere is regional web content available. Content can also be viewed from many places around the globe in services and websites. To identify your location, standard connections use local servers in the region. This ensures that when you are abroad, you cannot access information at home and cannot access foreign content from home. You can change to a server and essentially “change” your position with VPN location spoofing.
Secure data transfer: You might need to access sensitive files in the network of your employer if you operate on a remote basis. This type of data needs a safe link for security reasons. A VPN connection is also essential to obtain access to the network. To reduce the possibility of data loss, VPN services bind to private servers by using encryption techniques.
Network Security Concept No.7: Web Security
Web safety is often referred to as “cybersecurity.” In principle, it means security by identifying, blocking, or answering cyberattacks of a website or web application. Websites and mobile apps are just as likely to violate confidentiality as real homes, retailers, and public places. Cybercrime is unfortunate every day. To prevent websites and software apps from being hacked great precautions are required for web protection.
This is precisely what web security does – it is a mechanism for safeguarding steps and procedures that prevent unauthorized staff from hacking or entering your server or your web application. To secure blogs, Mobile Apps, and web services, this integral separation of information security is crucial. Anything that is used on the Internet should be protected by some kind of web encryption.

Why do we need this network security tool?
Web protection, regardless of how small or large the company might be, is one of the most critical aspects in operating through the internet, the LAN, or another system. While the Web is not attack-free, the protection of client data requires a secure and reliable Web security framework. An effective web safety scheme helps businesses reduce the chance of data stealing and sabotage being victims.
Web safety helps prevent malicious spyware for your workstations. It also guarantees the safekeeping of shared records. To deter the attacks of MiM by dividing information into numerous bits, encrypting certain parts, and sending them via separate routes, the web safety architecture avoids cases like eavesdropping.
Connecting to the internet means you get a lot of traffic. Huge traffic can create issues with reliability which may lead to system vulnerabilities. Web security promotes the stability of your website by constant surveillance of any suspect transactions which can sabotage the system, avoiding delays and downtimes.
Network Security Concept No.8: Wireless Security
Wireless security means preventing unwanted entry, disruption to machines and data using Wi-Fi networks. Wired privacy equivalent (WEP) and Wi-Fi Protected Access (Wi-Fi) are the most common form of safety (WPA). The WEP is an extremely poor safety standard: a simple device for the desktop and widespread coding applications will also be split into your password in a few minutes.
It was replaced in 2003 by WPA, or Wi-Fi Protected Access, by the old IEEE Specification 802.11 of 1997. WPA has become a fast alternative to enhancing WEP protection. The new model is WPA2; WPA2 cannot be supported without a firmware update or substitution by any hardware. WPA2 uses a 256-bit network encryption device that increases safety over WEP thanks to longer key lengths.
Companies also apply authentication to authenticate the connected computer using a certification-based scheme, according to the 802.11X protocol.
Why do we need this network security tool?
- Since many people are not luxurious enough to build their own homes from the start, a wired device cannot always be installed because it might not be preconnected to accommodate one in the home or the apartment. This is not to be said to be impossible, but surely it is harder to mount and cannot be achieved without the assistance of a licensed expert.
- Instead, it is very convenient to add wireless home safety. Typically, it consists of a control panel, configuring and installing wireless sensors on your doors and windows where you like your camera.
- Getting a smart home has become more popular in our increasingly digital society. Many people enjoy connecting their home safety systems conveniently through their other smart home systems or smartphone connections. It will switch on and off your safety system, or even monitor your cameras if you have an artificial intelligence system at home.
- Since the installation is simple, wireless devices are cheaper to install; most of them require only very specific DIY systems, or a representative from your protection company can install them easily. The wireless warning panels are normally battery-powered, so your power bill cannot work.
Network Security Concept No.9: Intrusion Prevention System
A network automated safety mechanism used to detect and respond to possible attacks is an intrusion prevention system (IPS). Like an IDS, an IPS detects potential risks by scrutinizing network traffic. Based on guidelines set by the network administrator, intrusion prevention systems manage the automatic response to a threat that an exploit can be performed very fast after the intruder achieves access.
The key duties of an IPS are to detect irregular activities, record information, block and report it.
Firewalls, antivirus applications, and anti-spleen software are used in IPS. Also, companies can use IPS to detect safety policy issues, track existing risks and prevent people from breaching safety policies for other reasons. In contemporary organizations, IPS has been a major component of a major security architecture.
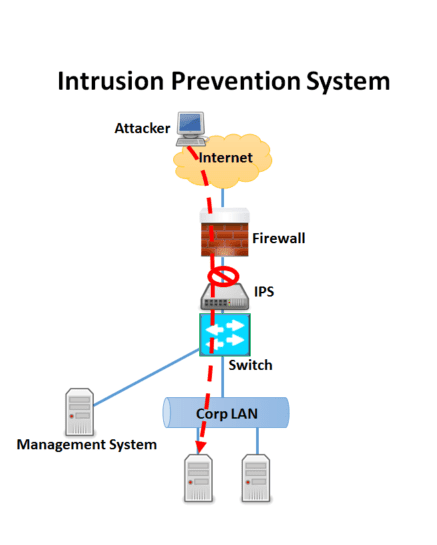
Why do we need this network security tool?
- Fewer cases of security. In general, the IPS means less interruption to university processes and a decreased number of safety injuries when the connected units do not note any improvements.
- Selective logging. Selective logging. The IPS tracks network operation only if it acts to protect network users’ privacy.
- Security and confidentiality. The Internet Protection System links network traffic to a catalog of documented malicious traffic and does not store or access contents.
- Fewer cases of security. In general, the IPS means less interruption to university processes and a decreased number of safety injuries when the connected units do not note any improvements.
- Selective logging. Selective logging. The IPS tracks network operation only if it acts to protect network users’ privacy.
- Security and confidentiality. The Internet Protection System links network traffic to a catalog of documented malicious traffic and does not store or access contents.
Network Security Concept No.10: Network Segmentation
Segmentation splits a network computer into smaller components. The aim is to increase the efficiency and safety of the network. The same words also mean division, partitioning of the network, and separation of the network. You cut it into smaller network sections as you break a computer network. In essence, you distinguish between different programs or implementations.
Both the servers and workstations are on the same local area network in a typical flat network (LAN). In most cases, these processes do not need to speak with each other or to “trust” each other. This is not necessarily important. Letting them connect only offers a hacker the possibility to swing from one device to another or to spread a piece of malware across your network.
Segmentation may either be performed physically or almost, but the outcome is identical. You restrict communication through your network and therefore limit the possible attack options. They can’t attack it if an intruder can’t see it.
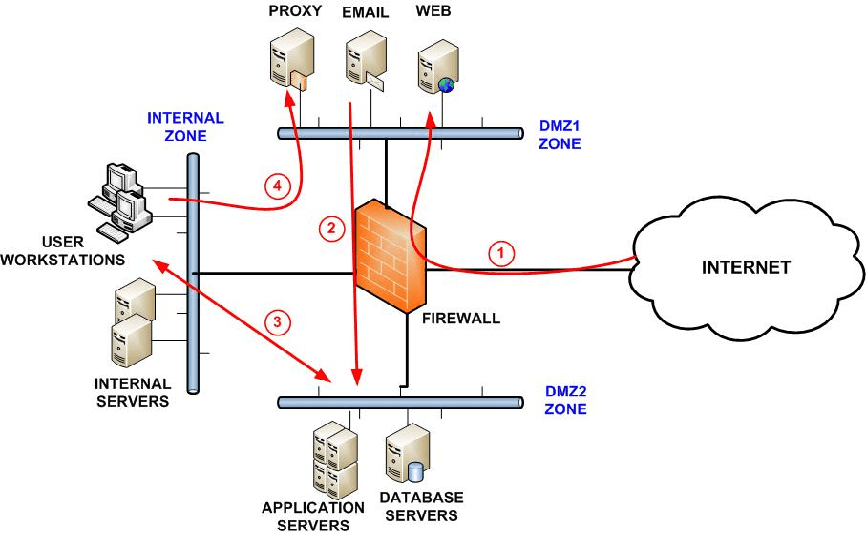
Why do we need this network security tool?
- Security enhanced. Network traffic can be segregated and routed so that connectivity to network segments is restricted and/or prevented.
- More Control of Access. Allow users to use only those network services.
- Enhanced surveillance. Opportunities to log incidents, control internal contacts enabled and rejected, and identify suspected behavior.
- Performance improvement. Local traffic is reduced with fewer hosts per subnet. The local subnet may be removed from broadcast traffic.
- Better confinement. Better containment. If there is a network issue, it has a limited impact on the local subnet.
Final Discussion
Network Security is an important aspect that all companies take into account. An attack or threat might cause an enterprise to lose substantial information or data. It can damage vital infrastructure as well. Therefore, a stable security strategy for the company’s network is the right choice.
Using these network security principles, the threats which the company can face in its operating environment can be mitigated significantly. Both security principles can ensure the confidentiality of information and data without compromising their availability or credibility.
About Writer
AB Rob
Founder & CEO